
Replacing HVAC System: Smart Features Guide
Traditional Thermostat Controls
In most legacy installations, control is handled through a single or dual-zone thermostat configuration, often one per floor… if that. These conventional setups operate on a simple call-for-heat or call-for-cool basis, with no zone-level control or occupancy-based logic. As a result, they rely entirely on user intervention to adjust setpoints, mode changes, or setback schedules.
For HVAC professionals, this translates to systems unable to adjust to shifting loads, occupancy, or solar gain from room to room. And the absence of temperature zoning and intelligent control logic leads to inefficiencies and inconsistent comfort delivery.
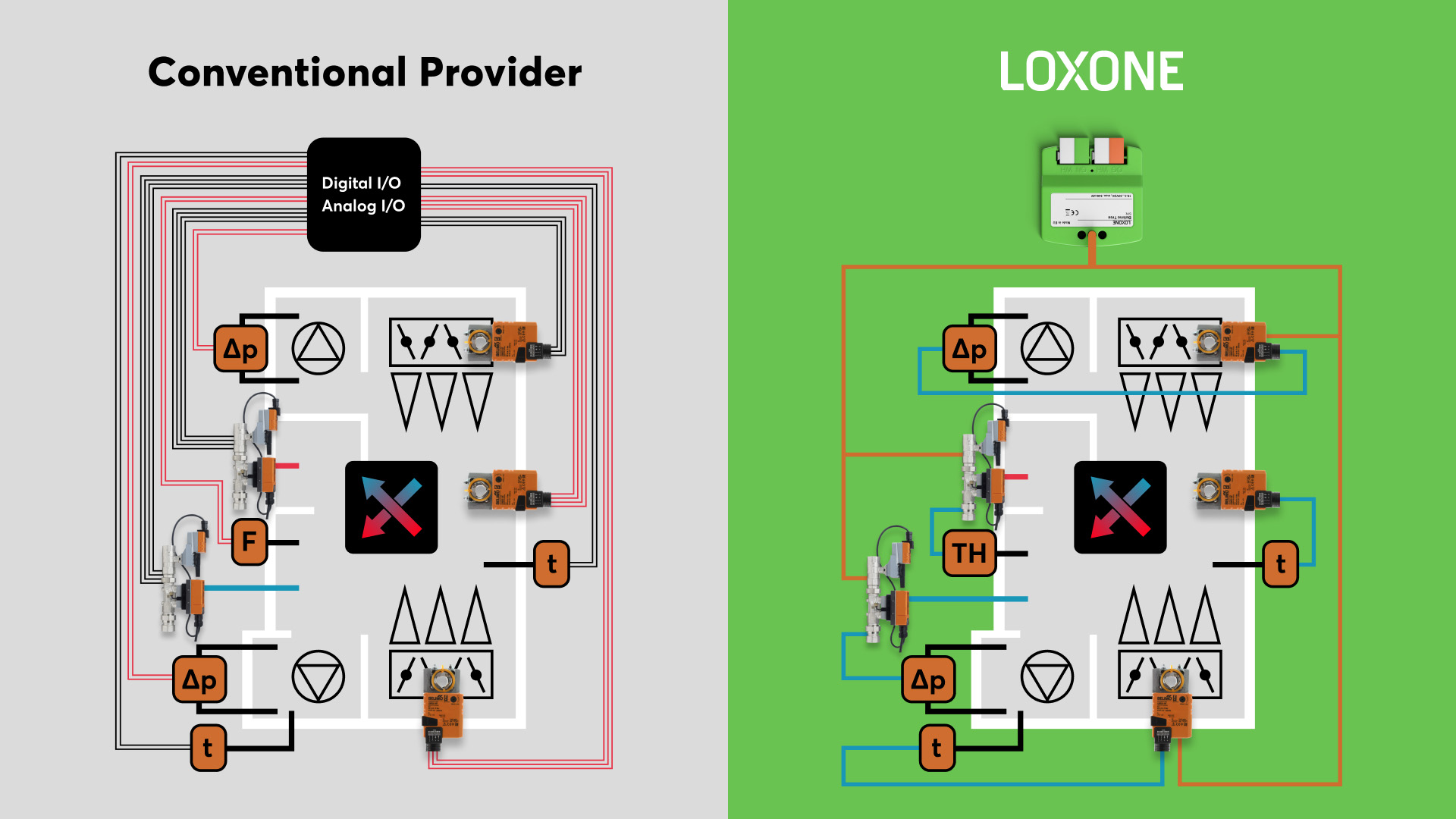
By contrast, Smart HVAC systems employ multiple sensors and digital control modules to manage temperature, humidity, and even air quality parameters on a per-zone basis. This allows for precise control of system output, improved balance across conditioned spaces, and measurable energy savings without a complete system replacement.
Limitations of Conventional Thermostats vs. Smart HVAC Systems
Standard thermostats don’t offer adaptive control or intelligent scheduling beyond basic setpoints. From an installation perspective, this limits your ability to optimize system performance or leverage occupancy patterns – features in high demand in high-end homes and buildings.
Integrating Smart HVAC systems with a central control platform, like Loxone, introduces advanced control logic that functions as a supervisory “brain” for the HVAC equipment. The system automatically adjusts setpoints, schedules heating and cooling based on occupancy detection, and adapts operation to maintain target climate across zones.
Drawbacks to Traditional HVAC Control

Unbalanced Heating and Cooling
Conventional thermostats typically use a single reference point, often a hallway sensor, to control the entire HVAC system. This results in uneven temperature distribution and comfort discrepancies across zones, which can indicate the need for zoning upgrades or integration with HVAC systems.

Manual Mode Switching
Traditional systems require manual toggling between heating and cooling modes to maintain comfort, which increases runtime and operational costs. Smart HVAC systems automate mode changes based on setpoint logic and ambient conditions, reducing unnecessary cycling and improving efficiency.

Limited Scheduling Flexibility
With standard thermostats, adjustments to heating and cooling schedules must be made individually at each device, with no occupancy-based logic. Smart HVAC systems allow centralized, presence-aware scheduling, enabling dynamic energy management without manual intervention.
6 Features for Controlling Smart HVAC Systems
By replacing conventional HVAC controls with a Loxone Miniserver integration, installers can enable a fully programmable HVAC control system. This setup allows for adaptive, self-learning temperature management based on occupancy, time schedules, and zone-specific setpoints.
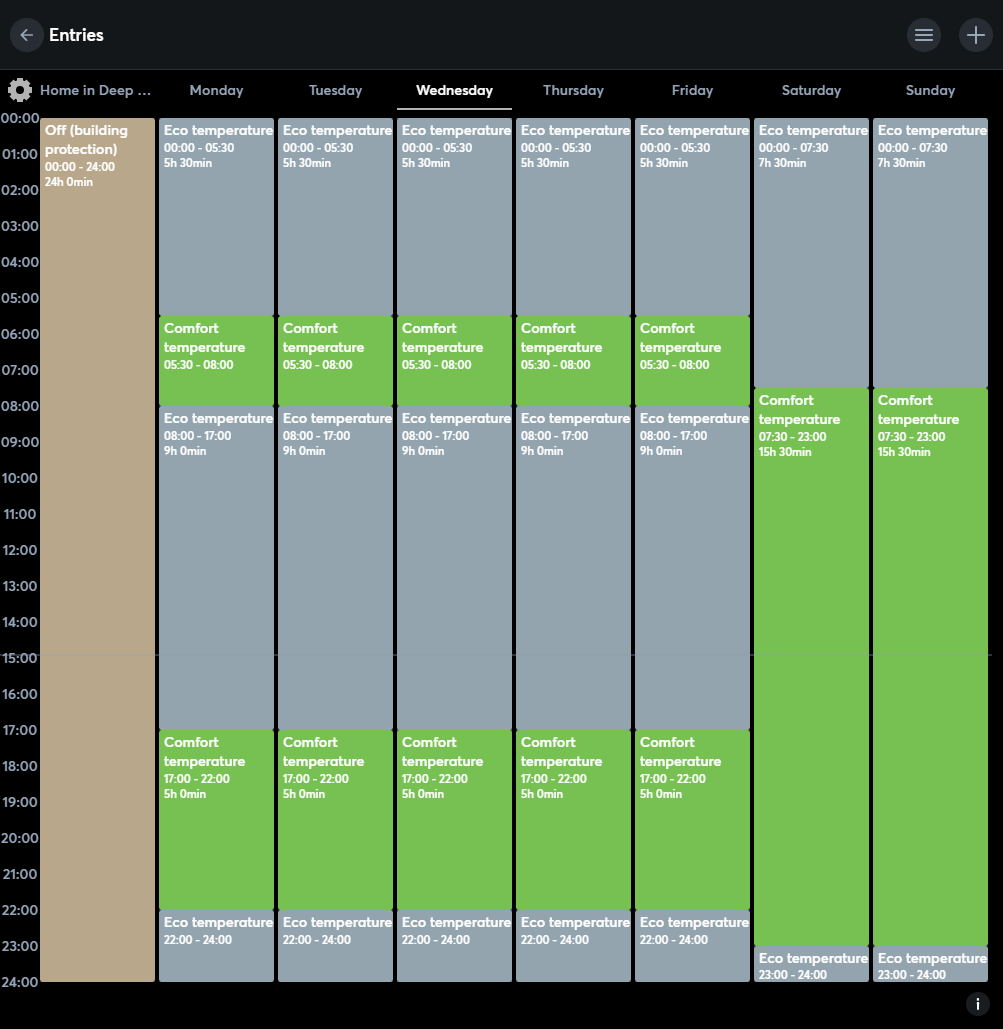
1. Eco Heating Schedules
With Smart HVAC systems integrated via the Loxone Miniserver, installers can configure centralized, zone-specific heating schedules for each day of the week via the Loxone App. This eliminates the need to adjust individual thermostats and allows precise control over runtime, setback periods, and energy optimization across all conditioned spaces.
2. Presence-Based Heating & Cooling
When no movement is detected in a zone for a set period (e.g., 30 minutes), the system reduces runtime by adjusting setpoints or entering Eco Mode. Upon detecting occupancy again, the system restores normal operating conditions. For installers, this demonstrates how sensor-driven automation can optimize energy usage while maintaining system responsiveness.
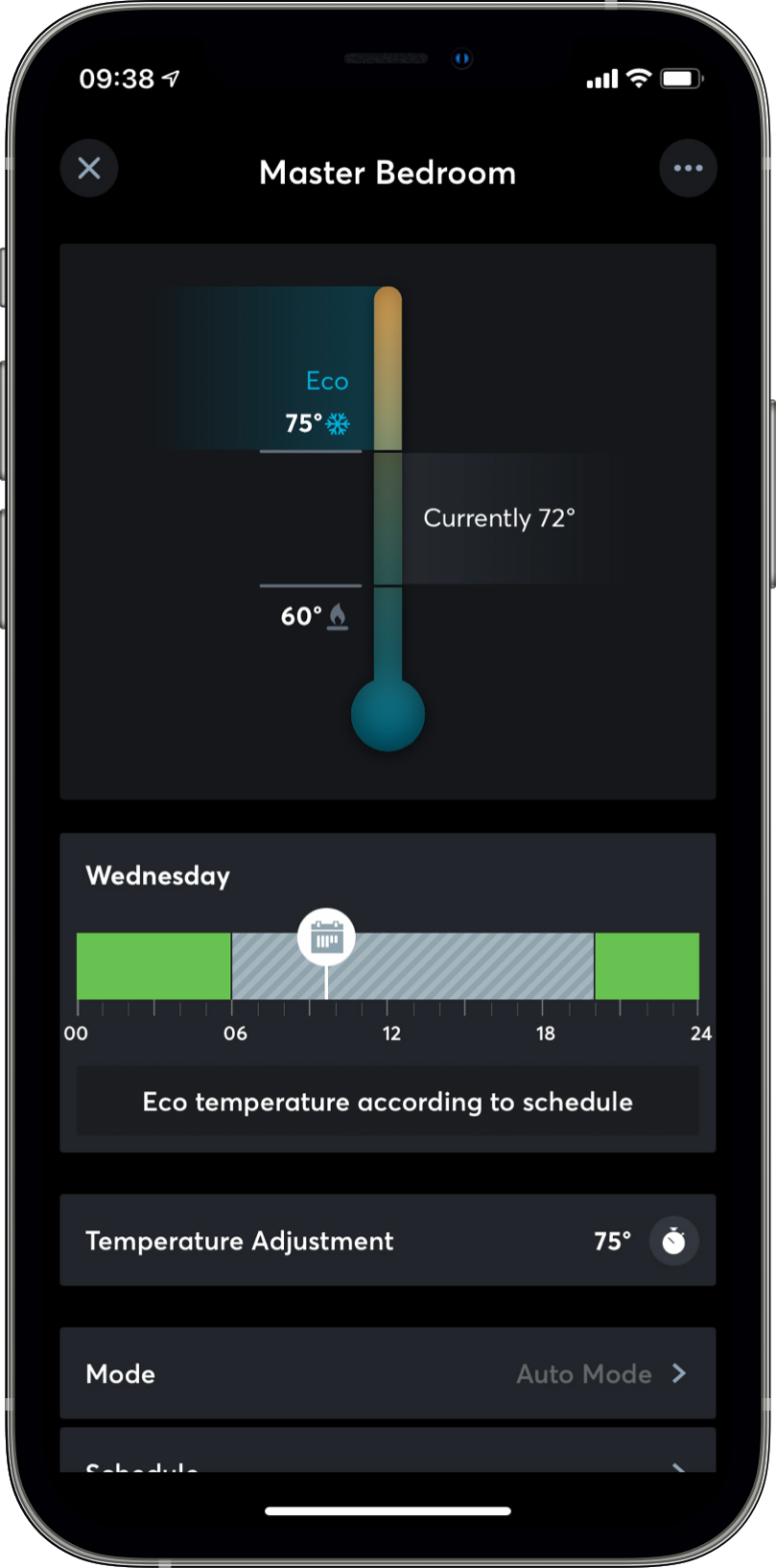
3. App-Based Control and Overrides
While HVAC systems integrated with Loxone operate autonomously through programmed logic and sensor feedback, manual control remains available via the Loxone App. Installers and users can remotely monitor system status, adjust setpoints, modify schedules, or initiate mode changes in real time. This provides a reliable interface for commissioning, diagnostics, and temporary overrides without requiring a physical thermostat.
4. Overheat & Frost Protection
Smart HVAC systems using the Loxone Miniserver continuously monitor room temperature via distributed sensors. Control logic enforces minimum and maximum temperature thresholds to prevent equipment damage or occupant discomfort. If a sensor detects conditions outside the defined range, the system can trigger protective actions (such as disabling heating or cooling stages) and send an alert for diagnostic review. This ensures stable operation and safeguards both the equipment and the conditioned space.
5. Precise Temperature Monitoring & Control
In a Loxone Smart HVAC systems temperature and humidity data is drawn from multiple sensors, like the Loxone Touch and Room Comfort Sensors, throughout the building. Control logic then calculates average zone temperatures and adjusts heating or cooling outputs to maintain precise setpoints. When excessive temperature differentials are detected, the system can activate circulation fans or dampers to balance distribution and improve efficiency.
Smart HVAC systems equipped with Loxone utilize adaptive learning algorithms to determine a building’s thermal response characteristics. Over time, the system learns how long it takes each zone to reach target under varying conditions. Using this data, the system can preheat or precool spaces so that the desired temperature is achieved at a scheduled time… optimizing comfort while minimizing runtime.

6. Zoned HVAC Control
HVAC systems can be configured for zoned operation using either motorized dampers in ducted systems or thermal/electronic actuators in hydronic or radiant setups. Through the Loxone Miniserver, each zone receives individual temperature feedback and control, allowing precise modulation of airflow or water flow based on real-time demand. This approach minimizes energy waste, prevents temperature imbalances, and ensures optimal comfort throughout the building, without requiring separate standalone thermostats for every area.
Hooking Up the HVAC system: Technical Details
To integrate an HVAC system with the Loxone Miniserver, follow these general steps:
- Power Down: Ensure the HVAC system is fully powered off before beginning any wiring.
- Thermostat Removal: Disconnect the existing wall thermostat and carefully pull back the thermostat wiring to the Miniserver location.
- Relay Connections: Connect the thermostat wires to the Miniserver outputs: one relay for fan control, one for heating stages, and one for cooling stages. Additional relays can be configured for multi-stage systems or auxiliary equipment.
Zone and room-level temperature monitoring is achieved via the integrated temperature and humidity sensors in Loxone Touch switches and wireless Loxone Temperature & Humidity Sensor Air units. This setup can also be extended to control radiant heating/cooling actuators or hydronic pumps with minimal additional wiring and configuration.